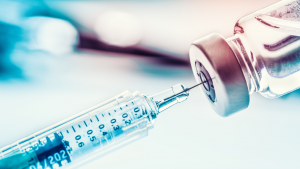
A pandemic is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of people. Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The most fatal pandemic in recorded history was the Black Death (also known as The Plague), which killed an estimated 75–200 million people in the 14th century.
The term was not used back then, but became popular for later outbreaks which include the 1918 influenza pandemic (Spanish flu).
WHAT IS A VACCINE?
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxins, or one of its surface proteins.
WHAT IS VACCINATION?
Vaccination is a simple, safe, and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases, before they come into contact with them. It uses your body’s natural defenses to build resistance to specific infections and makes your immune system stronger. Vaccines train your immune system to create antibodies, just as it does when it’s exposed to a disease. However, because vaccines contain only killed or weakened forms of germs like viruses or bacteria, they do not cause the disease or put you at risk of its complications. Most vaccines are given by an injection, but some are given orally (by mouth) or sprayed into the nose.
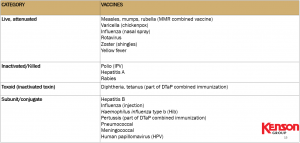
CATEGORIES OF VACCINES
There are several types of vaccines, each type was designed to teach your immune system how to fight off certain kinds of germs and the serious diseases they cause. When scientists create vaccines, they consider the following factors:
- How your immune system responds to the germ
- Who needs to be vaccinated against the germ
- The best technology or approach to create the vaccine .
The various categories of vaccines are:
- Inactivated
- Live-attenuated
- Messenger RNA (MRNA)
- Subunit, Recombinant, Polysaccharide and Conjugate
- Toxoid
- Viral vector
FUTURE OF VACCINES
Scientists are still working to create new types of vaccines. Some categories of vaccines currently being explored are:
- DNA Vaccines – These vaccines are easy and inexpensive to make. They produce strong, long-term immunity.
- Recombinant Vector Vaccines (Platform-based vaccines) – Act like a natural infection, so they are especially good teaching the immune system how to fight germs.
While we do understand that a number of persons are cautious when it comes to taking vaccines, here are some facts about getting vaccinated, in hopes that it will help members of the population to make well-informed decisions.

