National Renewable Energy Day
Boosting Sustainability
By Alyssa Jairam
1.0 SUMMARY
National Renewable Energy Day is observed annually on 21st March and brings awareness of the importance of renewable energy sources in fostering a sustainable and eco-friendly future. This research paper delves into the essence of renewable energy, highlighting its pivotal role, the array of global initiatives underway, the diverse forms of renewable energy available and the myriad benefits they offer. It culminates with various renewable energy projects worldwide that are exemplary in curtailing reliance on fossil fuels thereby broadening the energy mix and mitigating air pollution. Chosen for its profound significance, this topic underscores the indispensable contribution of renewable energy in diminishing greenhouse gas emissions, tackling climate change and fortifying global energy security. Through comprehensive research and exploration of various renewable energy initiatives and technologies worldwide, this study unveils a growing trend in harnessing solar and wind power for electricity generation. Remarkably, China leads with an impressive 1.161 GW from renewable sources followed by the US with a capacity of 352 GW. As we celebrate Renewable Energy Day, this paper advocates for the relentless dissemination of success stories in renewable energy advancements across the globe by individuals, organizations and governments. Such endeavours not only celebrate progress but also motivate collective action towards further innovations in the sector. This paper also encourages individuals to embrace electric vehicles (EVs) and integrate renewable energy technologies within their homes, thereby contributing to the global shift towards renewables which promises a healthier planet and a brighter future for generations to come.

Figure 1: National Renewable Energy Day is celebrated annually on 21st March | Source: Gexa Energy via X (formerly known as Twitter)
2.0 INTRODUCTION
Renewable energy, also known as Green Energy or Low-Carbon Energy refers to energy that is derived from natural processes and are replenished at a rate faster than they are consumed (United Nations, 2024). Unlike fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas which can take millions of years to form and are depleted when used, renewable energy sources are virtually inexhaustible and have a much lower environmental impact as compared to non-renewable energy sources.

Figure 2: Renewable vs non-renewable sources of energy. | Source: ADT
Renewable energy represents the foundation in the global transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly energy system due to its ability to replenish naturally on a human timescale. Renewable energy sources include solar, wind, biomass, geothermal and hydroelectric or hydropower which offer a clean and inexhaustible supply of energy (International Energy Agency, 2020). The pivot towards renewable energy is driven by the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, combat climate change and mitigate the environmental impacts associated with traditional fossil fuels. Renewable energy not only plays a critical role in achieving these environmental objectives but also contributes to energy security, economic growth and social development (Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century, 2021). By transitioning to renewable energy sources, societies can reduce their dependence on fossil fuels, decrease air pollution and create a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
National Renewable Energy Day is therefore dedicated to raising awareness and promoting the adoption of renewable energy sources worldwide whereby the essence of the celebration is universally aligned with the goals of enhancing public understanding and support for renewable energy. This day provides an opportunity for governments, organizations, educational institutions and individuals to engage in various activities such as seminars, workshops and renewable energy projects which are geared toward showcasing the advancements and potential of renewable energy technologies (United Nations Environment Programme, 2019).
3.0 PAPER OBJECTIVES
The objectives of this paper are to:
- Define renewable energy.
- Understand the significance of National Renewable Energy Day.
- Bring awareness of global initiatives in the promotion and adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Educate persons on the various sources of renewable energy.
- Show the global transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources for generating electricity.
- Educate persons on the benefits of renewable energy.
- Bring awareness of renewable energy projects worldwide.
4.0 SIGNIFICANCE OF NATIONAL RENEWABLE ENERGY DAY
The significance of National Renewable Energy Day is further underscored by its alignment with international efforts to address climate change and promote sustainable development, including the Paris Agreement and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). These global initiatives emphasize the critical role of renewable energy in reducing carbon emissions and achieving a sustainable future for all (UNFCCC, 2015).
At present, numerous global initiatives have been instrumental in promoting renewable energy adoption. For example, international agreements such as the Paris Agreement include ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the implementation and use of renewable energy technologies. Countries around the world are enforcing policies and programs to support renewable energy development which are leading to significant achievements in capacity growth, technology advancement and investment. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) plays a key role in facilitating cooperation and the sharing of knowledge among nations and countries.
Renewable energy and the observance of National Renewable Energy Day is therefore vital in addressing the global agenda for sustainability through the celebration of various achievements and fostering dialogue on renewable energy. This day contributes to the broader effort of transitioning to a sustainable energy future through innovations, collaborations and commitments to environmental stewardship.
5.0 SOURCES OF RENEWABLE ENERGY
The primary sources of renewable energy include:
- Solar Energy: This is energy captured from the sun using photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems. It is one of the most abundant and widely used forms of renewable energy which is suitable for electricity generation and heating applications.
- Wind Energy: This is energy generated by converting wind currents into electrical power using wind turbines. Wind energy is a clean, cost-effective and rapidly growing energy source.
- Biomass Energy: This energy comes from organic materials such as plants, wood and waste. When these organic materials are burnt or converted into biofuels, they release the energy stored in them from the sun.
- Geothermal Energy: This energy is generated by harnessing the heat from the Earth’s interior for heating and producing electricity. Geothermal power plants utilize steam which is produced from reservoirs of hot water that are located a few miles or more below the Earth’s surface.
- Hydroelectric Energy / Hydropower: This is produced by harnessing the energy of flowing or falling water. Hydroelectric energy is one of the oldest and largest sources of renewable power and is used for both large-scale electricity generation and small, off-grid applications.
Figure 3: Primary sources of renewable energy | Source: Millennium Engineers via LinkedIn
As seen on Figure 3 above, the use of renewable energy sources for generating electricity is increasing worldwide. In 2022, hydropower technologies generated 4,334.19TWh of electricity globally while wind and solar energy were used to generate 2,104.84TWh and 1,322.62TWh respectively. Other renewable energy sources such as geothermal and modern biofuels accounted for 776.86TWh giving a total of 8,538.50TWh being produced from renewable energy sources.
The increase in the use of renewables for electricity generation can be attributed to addressing environmental concerns since renewable energy sources emit little to no greenhouse gases and are more environmentally-friendly as compared to fossil fuels, technological advancements since renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines are designed to increase energy output while reducing costs and economic benefits due to the creation of jobs and stimulation of economic growth. Renewable energy also reduces the dependence on imported fuels while enhancing energy security and stability.
6.0 GLOBAL STATISTICS
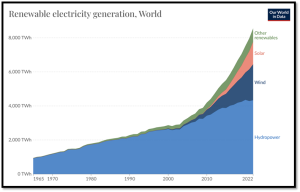
Figure 4: Global electricity generation using renewable sources | Source: Our World in Data.
As seen on Figure 4 above, the use of renewable energy sources for generating electricity is increasing worldwide. In 2022, hydropower technologies generated 4,334.19TWh of electricity globally while wind and solar energy were used to generate 2,104.84TWh and 1,322.62TWh respectively. Other renewable energy sources such as geothermal and modern biofuels accounted for 776.86TWh giving a total of 8,538.50TWh being produced from renewable energy sources.
The increase in the use of renewables for electricity generation can be attributed to addressing environmental concerns since renewable energy sources emit little to no greenhouse gases and are more environmentally-friendly as compared to fossil fuels, technological advancements since renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines are designed to increase energy output while reducing costs and economic benefits due to the creation of jobs and stimulation of economic growth. Renewable energy also reduces the dependence on imported fuels while enhancing energy security and stability.
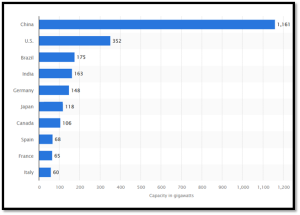
Figure 5: Leading countries in installed renewable energy capacity worldwide (2022). | Source: Statista
Figure 5 above shows the ranking of the top ten countries that use renewable energy sources for generating electricity. China is in the lead with 1.161GW followed by the United States with a generating capacity of 352GW and Brazil with 175GW. India is ranked fourth with 163GW and Germany with 148GW in the fifth position. Italy, France, Spain, Canada and Japan make up the remaining 5 countries with a generating capacity between 60-118GW from renewables.
7.0 DISCUSSION
7.1 Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy offers a myriad of benefits across environmental, economic and social dimensions. Some benefits of renewable energy include:
- Environmental Conservation: One of the primary benefits of renewable energy is its non-polluting nature as renewable energy sources emit little to no greenhouse gases or pollutants thereby significantly reducing air and water pollution. This therefore contributes to ecosystem conservation, climate change mitigation and meeting of international climate agreements and targets.
- Reduction of Greenhouse Gases: Renewable energy sources like solar, wind and hydroelectric systems generate energy without producing carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases which are major contributors to global climate change.
- Provision of Sustainable Energy: Unlike fossil fuels, renewable sources of energy like sunlight, wind and water are virtually inexhaustible. This sustainability ensures a long-term, stable energy supply for our present and future generations.
- Yielding of Energy Independence and Security: By utilizing local renewable energy sources, regions and countries can reduce their dependence on imported fuels for power generation. This therefore increases energy security, reduces the vulnerability to foreign energy supply disruptions and decreases trade deficits. Additionally, by diversifying energy supply sources, countries will enhance their national energy security.
- Stimulation of Economic Development: Renewable energy industries stimulate economic growth through the creation of jobs in various sectors such as manufacturing, installation, maintenance etc. These jobs are often localized and can be higher paying as compared to traditional energy sectors which contribute to improvements in the local economy.
- Increased Innovation and Investment: The renewable energy sector drives technological advancements which leads to more efficient and affordable energy solutions. This innovation not only attracts investments but also leads to increased economic benefits.
- Improved Health of Persons: Renewable energy production results in lower emissions of pollutants and particulates into the atmosphere which leads to improved air quality and public health by reducing respiratory diseases and cardiac health issues.
- Increased Energy Access: In remote, rural and underdeveloped areas, renewable energy can be a more feasible solution for power generation than extending traditional power grids. This can therefore improve living standards, increase education opportunities, improve energy access and foster socio-economic development.
- Price Stability: Renewable energy can offer more stable prices than fossil fuels which are prone to price volatility. At present, the cost of renewable energy technologies has decreased significantly which makes these technologies increasingly competitive with conventional energy sources. Thus, renewables are more cost effective and economically viable.
- Resilience: Distributed renewable energy systems can enhance grid resilience. For example, in the event of extreme weather events or other disruptions, having a diverse array of power sources can aid in maintaining a functioning electricity supply.
In summary, renewable energy presents a multifaceted array of benefits that address many critical challenges from environmental degradation and health risks to energy security and economic volatility.

Figure 6: Benefits associated with renewable energy | Source: Solar Calculator
7.2 Renewable Energy Projects Worldwide
7.2.1 Datong Super Energy Complex:
China is mitigating the environmental impacts of a former coal mine through a US$7.7 billion project in Shanxi province which is located South-West of Beijing. This facility will combine wind turbines, solar panels and battery storage in an old coal mining hub of Datong City which is expected to have 6GW of wind and solar capacity and 3.4GWh of energy storage. Construction on this new energy base commenced on 5th January, 2024 and is one of the 12 large-scale wind and photovoltaic power bases in China. These bases will contribute to realizing China’s ‘Dual Carbon’ goals which include:
- The peaking of carbon dioxide emissions before 2030.
- Going carbon neutral before 2060.
The project is expected to be completed and in operation by the end of 2025 with the transmission of 27 billion KWh of clean energy annually to Beijing and its surrounding areas via the Datong-Tianjin South Transmission Channel (China Daily, 2024). This project will therefore provide cleaner energy while ensuring that China moves closer to their sustainable development goals and achieving targets for climate change mitigation.
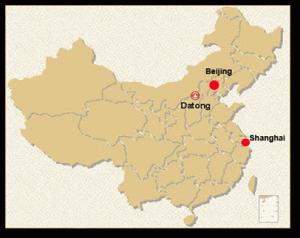
Figure 7: Location of Datong City, China where the Datong Super Energy Complex is being constructed | Source: Brigg and Janet.

Figure 8: A Road junction south of Datong, where the Super Energy Complex will join a cluster of traditional energy sources including coal and nuclear | Source: China Dialogue
7.2.2 Mojave Wind Farm:
The Mojave Wind Farm is also known as the Alta Wind Energy Center (AWEC) and is the third largest onshore wind energy project worldwide. This wind farm is located in Kern County, California in the United States and was commissioned in 1989. The Mojave Wind Farm is currently active and were constructed in multiple phases (Power Technology, 2024).
- Phase I: Consisted of 30 wind turbines which produced 18,000kW of power.
- Phase II: Consisted of 267 wind turbines with a total power of 66,750kW being generated (Wind Power, 2024).
Additionally, this wind farm boasts of a combined installed capacity of approximately 1,550MW of power generated which is sold to Southern California Edison under a 25-year old power purchase agreement (PPA).

Figure 9: A small portion of the Alta Wind Energy Center wind farm | Source: NS Energy
7.2.3 Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Station, UWI:
A new solar-powered charging station has been installed at the University of the West Indies, St. Augustine Campus. This charging station is accessible to the public for charging their electric vehicles. The EV charging station is powered by a 5-kilowatt solar photovoltaic system and complemented by a 24-kilowatt hour battery solution. This project therefore aims to take leadership in the new electric vehicle market by encouraging public charging locations which will assist in the continued adoption and growth of electric vehicles within the Trinidad and Tobago population. Hence, promoting cleaner transportation and a healthier environment (Trinidad Express, 2023).

Figure 10: The solar-powered electric vehicle (EV) charging station at UWI, St. Augustine. | Source: Trinidad Express Newspapers
8.0 CONCLUSION
National Renewable Energy Day embodies the collective aspiration for a sustainable and environmentally-friendly future powered by renewable energy. It is a day to celebrate progress, confront challenges and recommit to the global transition towards renewable energy sources by fostering awareness, encouraging innovation and facilitating collaboration. National Renewable Energy Day is therefore crucial in driving the renewable energy agenda forward and ensuring a healthier planet for future generations.
References
- “Climate Change.” 2024. Retrieved from World Health Organization (WHO): https://www.who.int/health-topics/climate-change#tab=tab_1
- “Emissions Gap Report.” 2019. Retrieved from United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): https://www.unep.org/resources/emissions-gap-report-2019
- “Mojave.” 2024. Retrieved from The Wind Power: https://www.thewindpower.net/windfarm_en_2837_mojave-16-17-18.php
- “New Energy Base Starts Construction in Datong City.” 2024. Retrieved from China Daily: http://shanxi.chinadaily.com.cn/datong/2024-01/11/c_955654.htm
- “New Solar-Powered EV Charging Station Installed at UWI.” 2023. Retrieved from Trinidad Express: https://trinidadexpress.com/business/local/new-solar-powered-ev-charging-station-installed-at-uwi/article_64156934-63e0-11ee-9ec9-c3fcf4d7ed0d.html
- “Power Plant Profile: Mojave Wind Farm.” 2024. Retrieved from Power Technology: https://www.power-technology.com/marketdata/power-plant-profile-mojave-161718-wind-farm-us/
- “Renewable Energy Benefits Leveraging Local Capacity for Onshore Wind.” 2017. Retrieved from IRENA.org: https://www.irena.org/publications/2017/Jun/Renewable-Energy-Benefits-Leveraging-Local-Capacity-for-Onshore-Wind
- “Renewable Energy Market Update.” 2020. Retrieved from International Energy Agency (IEA): https://www.iea.org/reports/renewable-energy-market-update
- “Renewables 2021 Global Status Report.” 2021. Retrieved from Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21): https://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/GSR2021_Full_Report.pdf
- Ritchie, Hannah. 2024. “Renewable Energy.” Retrieved from Our World In Data: https://ourworldindata.org/renewable-energy
- “Sustainable Development Goals.” n.d. Retrieved from United Nations: https://sdgs.un.org/goals
- “The Paris Agreement.” 2015. Retrieved from United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC): https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement
- “What Is Renewable Energy?” 2024. Retrieved from United Nations: https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/what-is-renewable-energy
